The worst side effect is osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), which is rare. ONJ is a side effect of bisphosphonates in general, not just alendronate. There were many lawsuits against Merck alleging ONJ injuries from people who took alendronate when Merck had the patent on it.
A 2008 paper in the Journal of the American Dental Association cast doubt on the alendronate-ONJ connection. The author found that people who took bisphosphonates intravenously had a higher risk of ONJ, but people who took them orally, as most do, had a lower risk. This was based on review of 700,000 cases. However, it is still widely believed in the medical field that ONJ is a possible side effect of alendronate because alendronate is so effective at stopping bone turnover.
Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been recognized for over a century. Indeed, there was an epidemic of Phossy Jaw in the second half of the 19th Century. Even at the time public health practitioners recognized the connection between yellow phosphorus (P4O10) workplace exposure and ONJ. Hence the name Phossy Jaw.
That epidemic of Phossy Jaw notably affected people who worked in match factories. Matches of the day used yellow phosphorus. It is believed that when the phosphorus oxide gets in the body, it reacts with amino acids and water and carbon dioxide to produce alendronate and other bisphosphonates. (Contrary to urban legend, no connection has been found between consumption of cola drinks - which contain phosphoric acid - and phossy jaw.)
Somewhat related to ONJ, severe bone and joint has been reported during bisphosphonate treatment. Pain might show up immediately after the medicine is started or several months later. Doctors have a range of options for dealing with osteoporosis, so be sure to speak up about any pain you experience.
Esophagitis, dysphagia, esophageal ulcers, esophageal erosions, and esophageal stricture have been reported with oral bisphosphonates.
This side effect shows up only after long usage of alendronate. This connection has only recently been described in the medical literature, and more research is needed to determine how common the fractures are and how much doctors should worry about them.
A report in the Canadian Medical Association Journal said that uveitis and sclentis (swelling of the middle and outer eye) were a problem particularly in new users of bisphosphonate drugs.
There was some thought that alendronate decreases the incidence of common fractures, but may actually increase the incidence of less common fractures. A report in the New England Journal of Medicine indicated that is not true.
Intravenous administration can make the patient feel like he/she has the flu and develop a fever. The white blood cell count may be diminished. This usually passes in a few days.
Some people get stomach cramps or other gastrointestinal problems (gastrointestinal mucosa irritation) on alendronate. While gastrointestinal problems are side effects of many drugs, with some medicines you can reduce these effects by taking the drug with a meal. Unfortunately, absorption of alendronate is poorer with food - this is one reason you shouldn't eat or drink anything for at least 30 minutes after taking the medicine.
Paget's disease patients taking 40 mg/day are more apt to get gastrointestinal problems than osteoporosis patients who take one pill per week.
Recently released documents indicate the pharmaceutical industry knew about concerns over alendronate safety years ago and that the FDA asked Merck to develop an osteoporosis drug that was safer than alendronate. Merck scientists knew that alendronate stayed in the body a long time and that this posed a potential risk.
A study published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute found evidence that taking bisphosphonates may help improve survival in breast cancer patients. Many breast cancer patients end up taking a bisphosphonate even if they have no bone issues because they are given an aromatse inhibitor to lower estrogen levels in the body (and reduce the risk of cancer recurrence) and the doctor worries the lower estrogen may result in bone loss. Scientists found that there was an association between taking bisphosphonates and lowwe rates of cancer metastasis. More research is needed before the medical community is going to recommend routine use of bisphosphonates for this purpose, however.
Over 10% of patients treated with risedronate have reported back pain, arthrolgia, abdominal pain, and dyspepsia. Severe upper gastrointestinal irritation can occur. Unfortunately, taking the drug with food is not a solution to this problem because absorption of oral bisphosphonates is even poorer when taken with food than when fasting.
Bisphosphonates result in lower blood calcium levels, and for most patients this is not a problem. Patients with vitamin D deficiency can experience problems; supplements of the vitamin are sometimes recommended.
Osteonecrosis, a rare jaw disease has been reported. Osteonecrosis has become a major concern with patients due to the severity of the condition. This rare jaw disorder is seen in cancer patients who were treated with radiation to the head and neck. This disease is difficult to treat and requires multiple surgeries and antibiotics. The incident of bisphosphonates causing osteonecrosis is less then 0.1%. Some patients have reported that their dentists have told them to discontinue the use of bisphosphonates, because of the severity of the disease. However the American Dental Association has recommended not to discontinue this medication. There are anecdotal reports of dentists seeing more osteonecrosis cases possibly due to more patients on long-term therapy.
Less common reactions to Risedronate are bone, joint and muscle pain. All bisposphonates may interfere with bone imaging agents. Patients should report to physicians that they are taking risedronate prior to any type of bone imaging.
Uveitis and sclentis (swelling of the eyes) are other potential side effects.
Side effects are a concern with all medications and nearly all drugs have adverse reactions when compared to placebo. Overall, risedronic acid is well tolerated and not as much of a concern as many other prescription drugs.
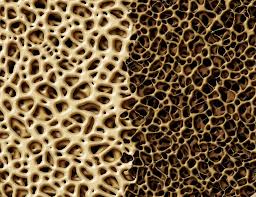
Bisphosphonates block bone resorption. They have been widely used for years and although there can be side effects, the medical profession considers them generally safe and effective. More
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs) are chemical compounds that act on the estrogen receptors in the body. More.
